Planting Coins: the first report from our crypto portfolio
Management Summary The crypto investing series starts under adverse market conditions. Our investment strategy was able to compensate or dampen...
Please click on the blue "+" sign to open the full menu.
We have the right products for you, for a secure future.
We provide you with the right advice, to be future-proof.
It all starts with a friendly conversation. Just contact us.
6 min read
 Markus Abbassi
:
December 20, 2022
Markus Abbassi
:
December 20, 2022
This blog post is the third reporting since the initiation of our crypto portfolio, and the fourth part of our crypto investing series Planting Coins. Read more about our crypto portfolio framework here. Don't forget to sign up for our newsletter to get the next reporting straight in your mailbox!
These days there is mainly one topic in the technology world: ChatGPT, a Generative Pre-trained Transformer language model developed by OpenAI. As a technologically interested and innovative private bank, we decided to test the availability of this chatbot in terms of its capabilities and limitations, using the topic of staking as an example, and therefore decided to conduct an interview with ChatGPT. The interview with ChatGPT was conducted on December 19, 2022. For readability, some answers have been shortened.
Kaleido: Dear ChatGPT, you are a real multi-talent. What's your current take on blockchain and cryptocurrencies?
ChatGPT: While blockchain and cryptocurrencies have the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries, they are still in the early stages of development and adoption. As with any emerging technology, there are also significant risks and challenges that need to be addressed, including regulatory issues, security concerns, and market volatility.
Kaleido: Agreed, now let's move on to our topic for today, Staking. What is Staking?
ChatGPT: Staking is the process of holding a certain number of coins or tokens in a cryptocurrency wallet and participating in the validation of transactions on a blockchain network. In return for staking their coins and helping to secure the network, users can earn rewards in the form of new coins or tokens.
Staking is a way to earn passive income with cryptocurrency, and it can be a way to increase one's holding of a particular cryptocurrency without having to buy more coins. It can also be a way to support the security and stability of a blockchain network by providing additional resources for validating transactions.
Kaleido: As you know, there are different staking methodologies. Which are the three most common?
ChatGPT: There are actually several different ways to stake coins or tokens, depending on the particular blockchain and the staking mechanism it uses. Here are three common types of staking:
It's worth noting that there are many other types of staking mechanisms in use, and the specific details of how staking works can vary significantly from one blockchain to another.
Kaleido: Malicious tongues claim that staking is just an inflation compensation, what do you say to that?
ChatGPT: It's true that staking can be a way for users to earn rewards for helping to secure and support a blockchain network. In some cases, these rewards may take the form of new coins or tokens that are generated through the process of block validation, which can lead to an increase in the overall supply of the cryptocurrency. This increase in supply can be seen as a form of inflation, as it can dilute the value of the existing coins or tokens.
However, it's important to note that staking is not the same as simple inflation, as it involves a real economic activity – namely, the validation and security of transactions on a blockchain network. Staking is often used as a way to incentivize users to contribute their resources and participate in the network, and it can also help to decentralize the network and make it more secure.
Kaleido: Are there any other disadvantages besides the inflation issue with Proof of Stake?
ChatGPT: There are a few potential disadvantages to the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm that it's worth considering:
Kaleido: But surely staking also has significant advantages over other validation mechanisms?
ChatGPT: Yes, staking – particularly proof-of-stake (PoS) – does have a number of advantages over other consensus algorithms. Here are a few examples:
Kaleido: So which validation mechanism will prevail in the long run?
ChatGPT: It's difficult to predict which validation mechanism will prevail in the long run, as the adoption and use of different consensus algorithms can vary significantly over time and across different blockchain networks.
Both proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS) have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the most appropriate mechanism will depend on the specific needs and goals of the blockchain network in question. PoW systems, which are used by cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, are well-established and have a strong track record of security and decentralization, but they can be energy-intensive and may not be well-suited to high-throughput environments. PoS systems, on the other hand, are more energy-efficient and scalable, but they may be less secure and more prone to centralization.
There are also many other types of consensus algorithms in use or under development, including delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), delegated Byzantine fault tolerance (dBFT), and proof-of-authority (PoA), each of which has its own unique set of characteristics and trade-offs.
Ultimately, the adoption and use of any particular consensus algorithm will depend on a range of factors, including the needs of the network, the preferences of the users, and the overall state of the technology. It's possible that different consensus algorithms may coexist and be used for different purposes, depending on the specific requirements of the network.
Kaleido: Thank you very much ChatGPT for sharing these valuable insights on staking.
ChatGPT: You're welcome! I'm glad that I could help. If you have any further questions about staking or any other topic, don't hesitate to ask. I'm here to help!
The portfolio was launched on November 2, 2022 at 7 p.m. CET, just before the events surrounding the FTX crypto exchange. The data of this report is as per December 20, 2022 at 7:30 a.m. CET.
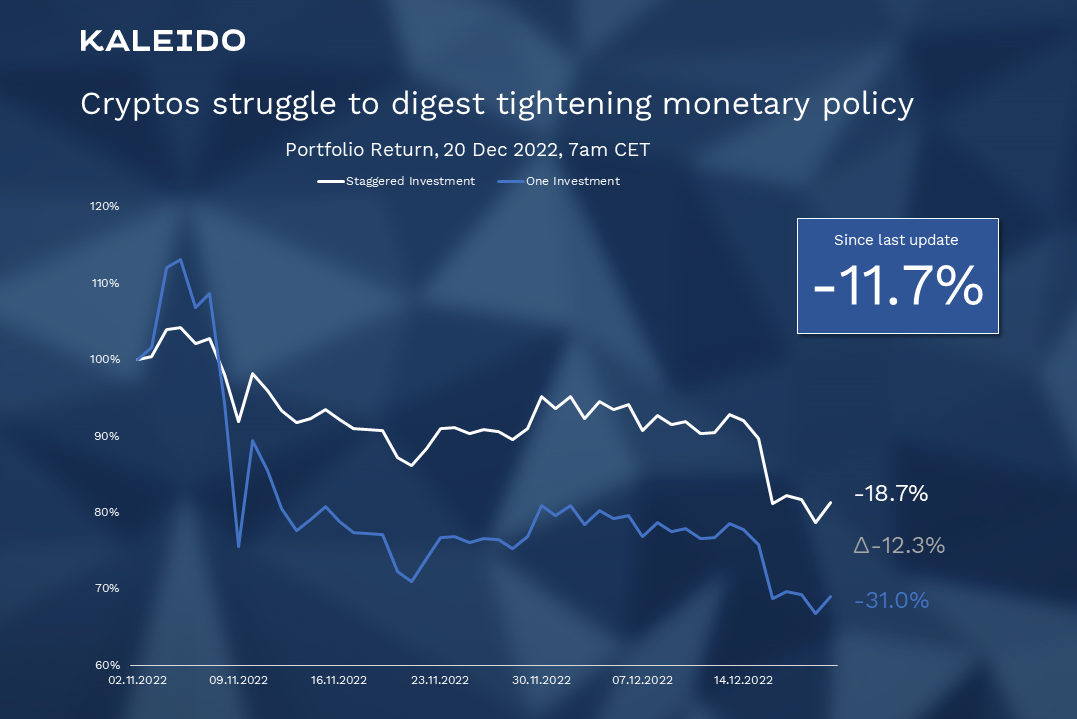
Figure 1: Cryptos struggle to digest tightening monetary policy.
After six weeks, the portfolio shows a negative performance of -18.7 %, compared to -7.0 % two weeks ago. The loss of another 11.7 % is mainly due to the negative market reactions to the recent central bank announcements regarding further monetary tightening, but also to rumors about possible liquidations of crypto funds, which strongly affected younger coins such as Near Protocol.
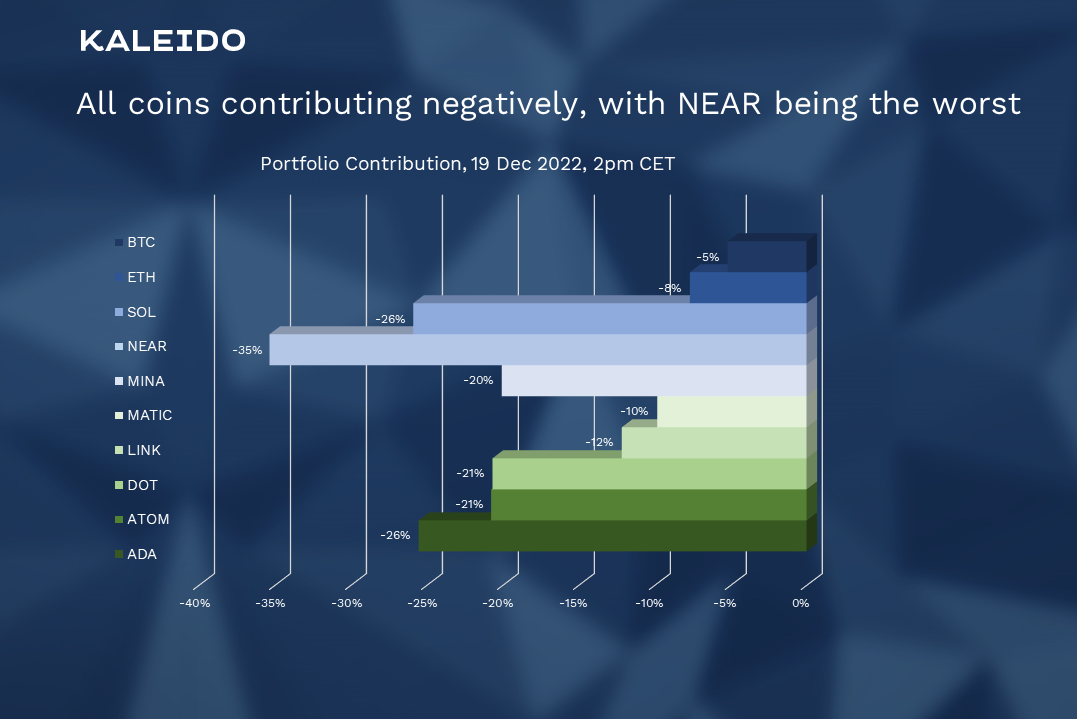
Figure 2: All coins contributing negatively, with NEAR being the worst.
The current look at portfolio contributions shows relatively clearly that BTC and ETH are the real blue chips in the portfolio. MATIC has also not performed badly so far, but has given back much of its performance.
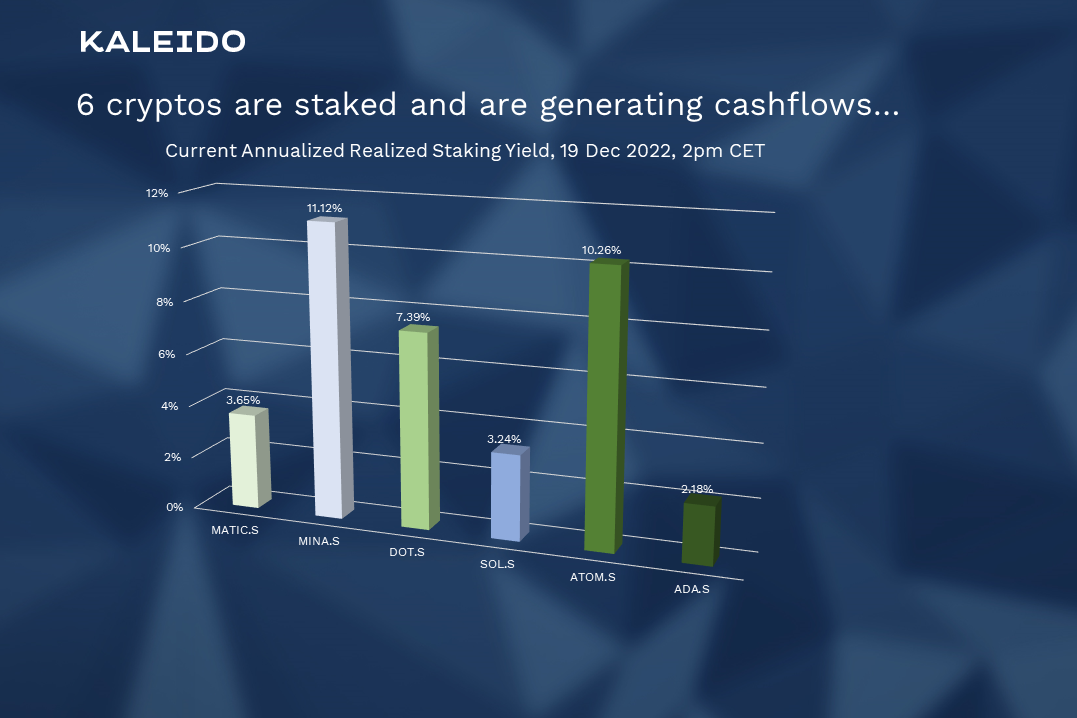
Figure 3: Six cryptos are staked, generating cashflows…
The replication of the portfolio on the crypto exchange Kraken currently allows for the staking of six coins, although the NEAR protocol is not yet technically supported, and the staking of ETH is waived due to liquidity issues since the withdrawal mechanism is not yet available.
Staking rates are calculated on an annual basis based on the effectively realized staking rewards on a daily basis. Thus, they vary on a daily basis, but give an approximate indication of what to expect.
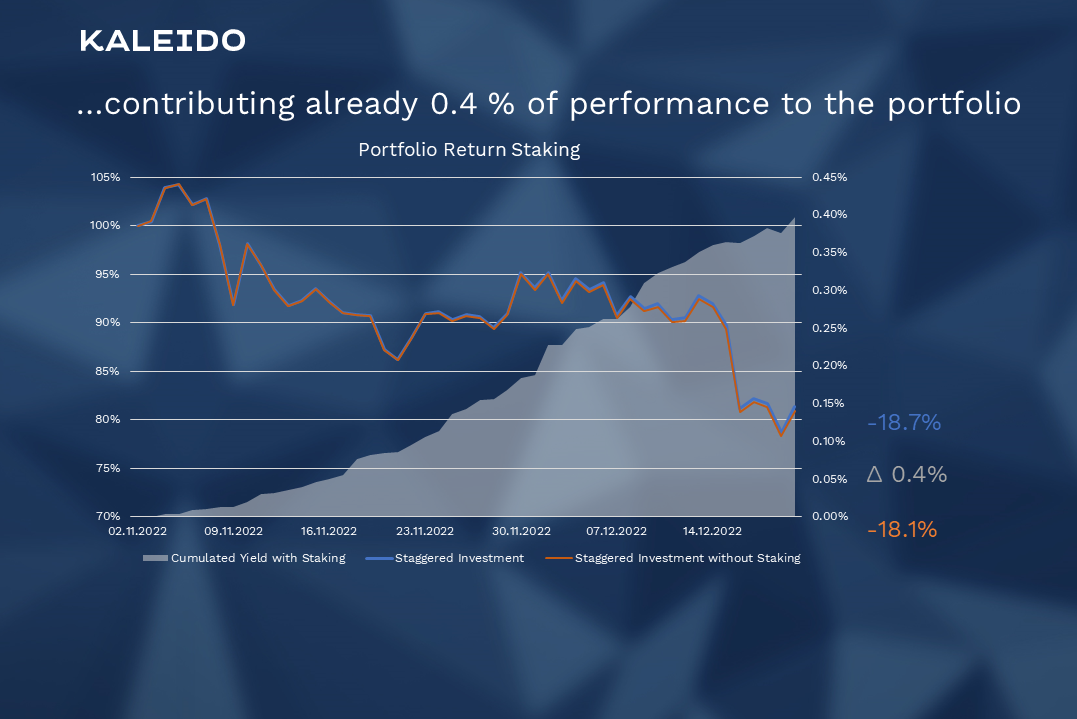
Figure 4: …contributing already 0.4 % of performance to the portfolio.
Of course, the staking rates have to be put into perspective with inflation, but in today's view it is first about how much the decision against staking would cost our portfolio. As figure 4 shows, we could already achieve 0.4 % performance with the decision to stake the six currencies.
This blog post is written by Markus Abbassi, Head of Digital Assets at Kaleido Privatbank AG. If you have any questions regarding crypto investing, or wish to get in touch with Markus, you can contact him here.
Disclaimer: This piece of information is for marketing and entertainment purposes only and should not be taken as investment recommendation. Remember that all investments involve risk. Please read our full Marketing Disclaimer here.

Management Summary The crypto investing series starts under adverse market conditions. Our investment strategy was able to compensate or dampen...

2 min read
Management Summary Today's focus is on various portfolio construction strategies: lump-sum investment, market timing, staggered, or Dollar Cost...

Management Summary After a great start into 2023, our Crypto Garden portfolio is currently at 120.4 points. In March, we observe a strong rise in...